High-Throughput Synchronous Deep RL
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC)
Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020
Abstract
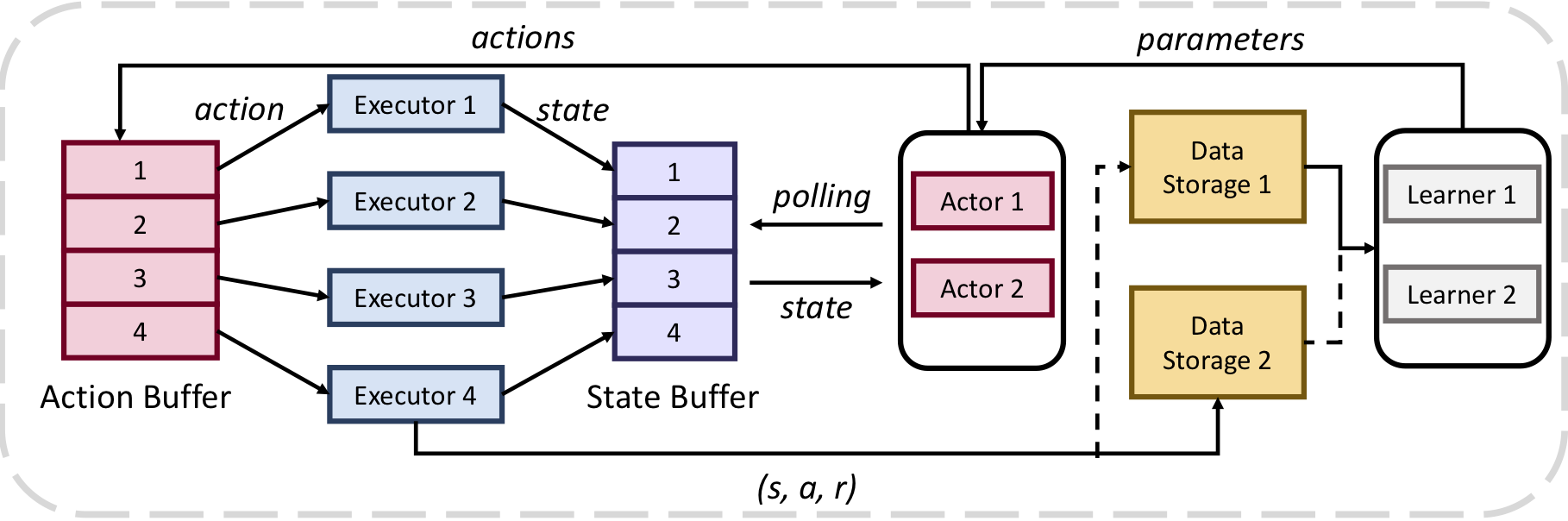
Various parallel actor-learner methods reduce long training times for deep reinforcement learning. Synchronous methods enjoy training stability while having lower data throughput. In contrast, asynchronous methods achieve high throughput but suffer from stability issues and lower sample efficiency due to ‘stale policies’. To combine the advantages of both methods we propose High-Throughput Synchronous Deep Reinforcement Learning (HTS-RL). In HTS-RL, we perform learning and rollouts concurrently, devise a system design which avoids ‘stale policies’ and ensure that actors interact with environment replicas in an asynchronous manner while maintaining full determinism. We evaluate our approach on Atari games and the Google Research Football environment. Compared to synchronous baselines, HTS-RL is 2 − 6X faster. Compared to state-of-the-art asynchronous methods, HTS-RL has competitive throughput and consistently achieves higher average episode rewards.
Materials
Presentation
Citation
@inproceedings{LiuNEURIPS2020,
author = {I.-J. Liu and R.~A. Yeh and A.~G. Schwing},
title = {{High-Throughput Synchronous Deep RL}},
booktitle = {Proc. NeurIPS},
year = {2020},
}
Acknowledgement
This work is supported in part by NSF under Grant # 1718221, 2008387 and MRI #1725729, NIFA award 2020-67021-32799, UIUC, Samsung, Amazon, 3M, Cisco Systems Inc. (Gift Award CG 1377144), and a Google PhD Fellowship to RY. We thank Cisco for access to the Arcetri cluster.